What Is an AI Model?
An AI model is a system trained to recognize patterns, make predictions, or generate new content using data. It learns by analyzing examples and adjusting internal parameters to minimize errors. Models come in many types—classification, regression, generative, and more—each designed for different tasks. From chatbots to image recognition, AI models power nearly every modern intelligent application. Understanding what a model is helps you see how AI systems process information and respond intelligently.
How Models Learn

AI models learn through a process called training. During training, the model studies large amounts of data and attempts to predict outputs. When it's wrong, an algorithm adjusts the model to improve accuracy. Repeating this millions of times helps the model understand patterns deeply. This process is similar to humans learning from mistakes. Good training requires clean data, the right model architecture, and techniques that prevent overfitting or bias.
Training vs Inference
Training is the phase where the model learns from data using heavy computation. It often requires GPUs, large datasets, and long hours of optimization. Inference happens after training—when the model is used to make predictions or generate output in real time. For example, when you chat with an AI assistant, you are using inference. Understanding the difference helps developers build efficient systems that can learn effectively yet run smoothly for users.
Why Model Architecture Matters
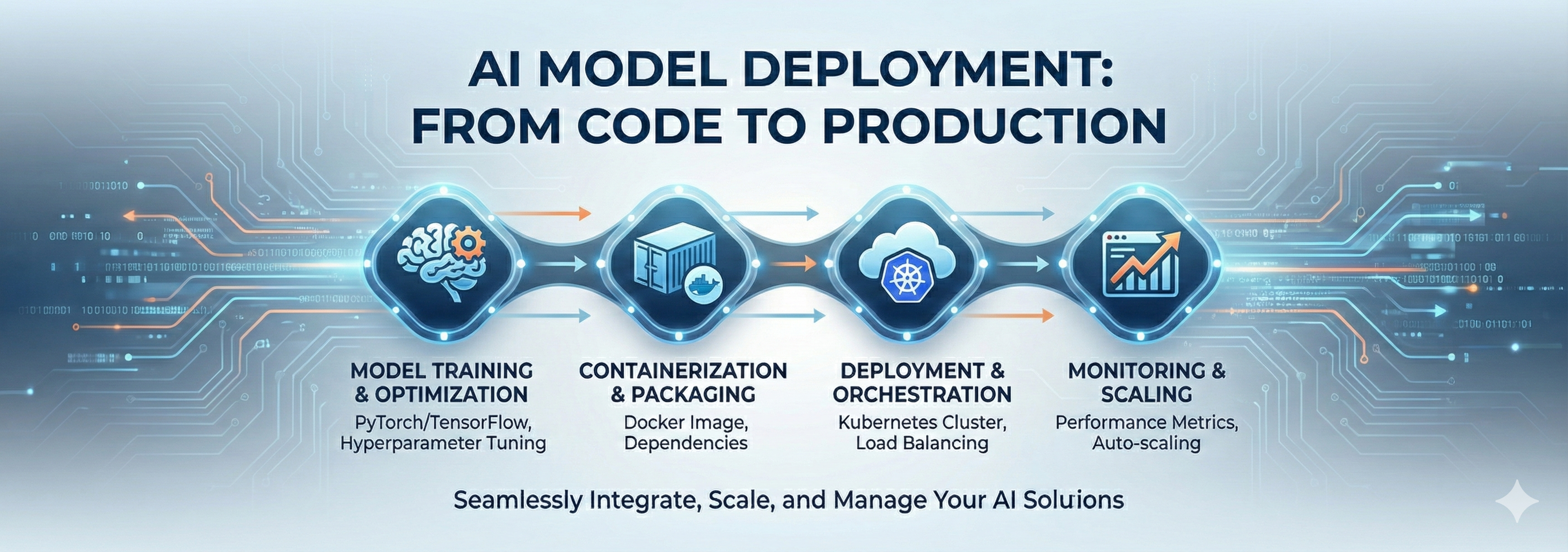
Model architecture defines how an AI model is structured—how its layers connect, how data flows, and how it processes input. Architectures like CNNs, RNNs, and Transformers each specialize in different tasks. A strong architecture improves accuracy, speed, and generalization. As AI evolves, new architectures push the boundaries of what machines can understand and create. Knowing about architectures helps you choose the right model for your projects and gives insight into how advanced AI works internally.



